The world has turned digital. This digitalisation has made everything simpler, even payments.
Transactions as small as paying for a coffee, or heavy transactions like making payments for your business, can all be done conveniently with a tap on your smartphone.
This is not limited to individuals. Running an online business, too, has become easier because online transactions, be it with a vendor, partner, or customer, have become hassle-free.
This shows in the latest data by India’s Ministry of Finance, which suggests that digital transactions have surged with over 18,000 crore transactions in 2024-25.
As fast and easy as it may seem, there is an incredible amount of technology that works behind the scenes. It ensures that your money moves securely and accurately from your account to the merchant’s account.
A digital payment processing platform enables this entire ecosystem
What is a Payment Processing Platform?
It is like a backbone that handles authorisation, security, fraud checks, clearing, and settlement. It enables businesses to accept, authorise, process, and settle electronic payments securely and efficiently.
Making payments through simple card swipes, mobile or online checkouts, all of it happens in a flash. All thanks to a payment processing platform that coordinates multiple entities like banks, networks, security systems, and compliance frameworks. All done within seconds.
Simply put, these platforms act as an intermediary between the merchant, the customer, and financial institutions.
This article aims to show the steps and depth of the payment process that look effortless and short on the surface level.
Key Players and Components of the Digital Payment Process
Before understanding the process, it is necessary to understand the key elements that make the entire system possible.
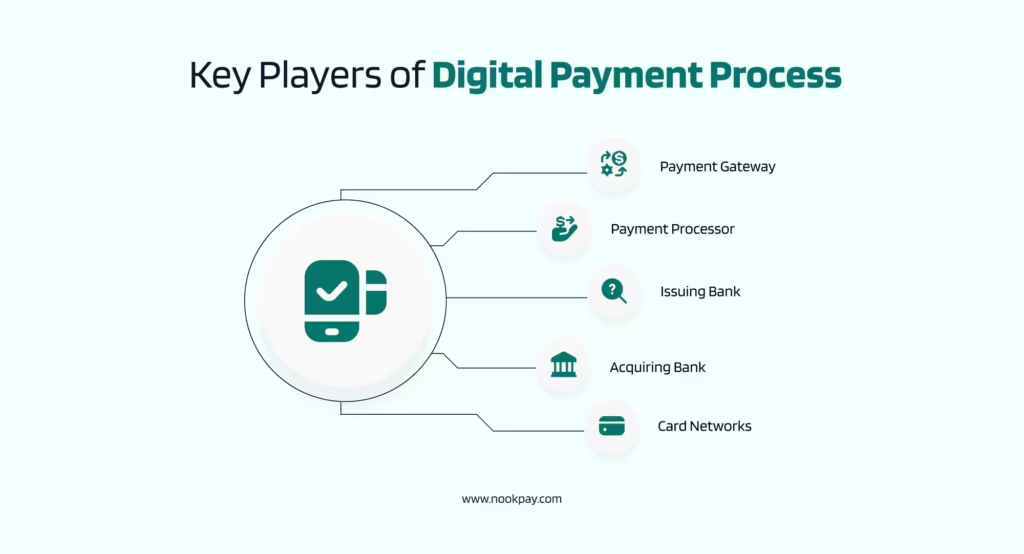
A digital payment processing platform is not just a single tool that does all the work. It is more like a well-coordinated system where every component has a role to play to ensure that the payment goes smoothly. These elements include:
Payment Gateway
It is like a secure entry point for the transaction journey. As the card details are entered and the payment method is selected, the gateway captures that information. It is then forwarded for processing.
It is like a digital cashier, and its role is to ensure that all the sensitive data is passed safely and quickly without exposure or leaks.
Payment Processor
As the gateway sends the data forward, the payment processor takes over.
The job of a payment processor is to:
- Direct the transaction to the right places
- Communicate with banks
- Manage all the back-and-forth tasks to get an approval or a decline
Then the processor ensures:
- Request reaches the customer’s bank
- Waits for the response
- Response relayed to the merchant
Without the processor, the payments would get stalled before even reaching the banking system.
Issuing Bank
The issuing bank’s role is to serve the customer and hold their account. It makes sure that the account is valid and that the account has enough funds or credits.
Once everything is confirmed to be in place, the issuing bank approves the payment and keeps a temporary hold on the amount
Acquiring Bank
The acquiring bank is a part of the other side of the transaction, which works with the merchant. These banks receive approved transactions, and once the settlement is done, they deposit the funds into the merchant’s account.
While the issuing bank’s role is to protect the customer, the acquiring bank is supposed to ensure that the businesses receive payments correctly and on time.
Card Networks
Mastercard and Visa are commonly seen names on cards and transaction platforms. But what exactly are they?
They are network cards that connect banks, merchants, and cardholders to authorise and process transactions. One must not confuse them with card issuers, like banks.
They set rules and manage the infrastructures that enable payments. Additionally, they also offer different perks and acceptances based on their brand and partnerships.
Types of Digital Payment Processing Platforms
Not all payment processing platforms serve the same purpose. Hence, they can be divided into broader categories on the basis of their use cases and payment direction.
Inbound Processing Platforms
These platforms collect payments from customers. Common examples of these include:
- Online store checkouts
- Billing for subscription-based services
- Mobile app payments
Outbound Processing Platforms
These platforms are responsible for sending out money to third parties. They are mostly used for:
- Vendor payments
- Affiliate Commissions
- Creator or partner payouts
Its primary focus remains on:
- Validating invoices
- Compliance and approvals
- Bulk payments
End-to-end Payment Platforms
Some platforms manage both inbound and outbound flows. They are mostly used by:
- Marketplaces
- Fintech products
- Platforms managing user balance, such as digital wallets or prepaid systems
As compared to the other systems, this system is more complex. This is because it keeps track of the money that is coming in and going out across multiple parties.
The Flow of Processing a Digital Payment
What is instant for the users actually happens in distinct stages.
The cycle of payment begins with initiation, where the customer, or vendor (in the case of B2B) shares their bank account details. It is then encrypted and transmitted to a payment gateway, which converts the data and forwards it to the payment processor.
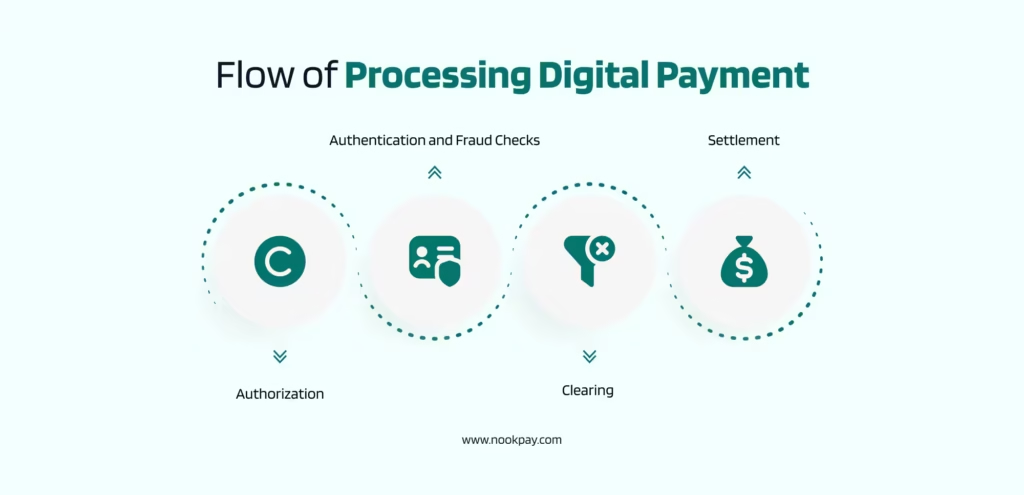
This is where the major role of a payment processor comes into play. It begins with the following steps.
Authorization
It is the platform’s way of asking, “Is this payment allowed?”
The payment processor sends the transaction details to the respective banks after completing all the checks. The payment processor verifies whether the payment method is valid and checks for the availability of funds and credits.
Authentication and Fraud Checks
The verification process is only complete once fraud detection and authentication is done. Some primary examples of this include –
- Behavioural checks like those of location, device and transaction patterns
- App-based confirmation
- One-time passwords
It is after these validations that the transaction is finally good to go. All these safeguards aim to reduce fraud without disrupting the user experience. A good digital payment processing platform ensures that a balance between security and speed is maintained.
Once the transaction is approved, the customer receives a “payment successful” message. Though, it is important to note that the money hasn’t actually moved yet.
Clearing
In this step of the process, the funds are prepared to move.
Clearing is a behind-the-scenes process where approved transactions are collected and verified. It is at this stage that the transaction details are recorded and matched across the systems.
It is only then that the fees are calculated and records are prepared for settlement. This step is meant to ensure that all the parties involved agree to the transaction before the funds are actually transferred.
Settlement
It is when the money is actually transferred to the receiver. Depending on the region and mode of payment –
- Settlement may happen instantaneously
- Or it may take a few business days
When completed, the transaction cycle is finally completed and closed.
Security and Compliance
One of the major concerns for customers is that their payment details must remain private. Businesses, on the other hand, are concerned about the legitimacy of the transaction.
Security, hence, becomes foundational to every digital payment processing platform. It is not just a mere add-on, but a baseline security requirement.
Digital payment processing platforms are designed in such a way that they quietly take care of the risks in the background.
PCI DSS Compliance
Following this compliance is like a ground rule for card payment. If a platform processes card payments, PCI DSS compliance is a non-negotiable requirement.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of guidelines that outline the requirements for handling, storing, and transferring cardholder data.
In simpler terms, these guidelines aim to make sure that –
- Card details are not exposed or maintained casually
- Sensitive data is not easily accessible and is tightly controlled
- Systems are regularly monitored to identify weak points
Using PCI-compliant platforms reduces the chances of a data breach and maintains a sense of reliability with customers, banks, and card networks.
Encryption and Tokenisation
Exposure of data means higher chances of data exploitation, and that is one of the biggest fears in digital payments. To prevent this, payment platforms depend on two methods:
- Encryption – It jumbles the payment data while it’s being transmitted. This way, even if someone is able to seize the data, the information will remain unreadable.
- Tokenisation – it is a process of converting data into small units for easier processing, analysis, or security. It replaces sensitive data, such as credit card details and personally identifiable information, with a unique and non-sensitive token.
This keeps the data safe and ensures that it is not misused outside the system.
Fraud Detection Systems
Data leakage does not necessarily have to be the only threat. Some threats also come from fraudulent transactions that may not seem to be suspicious in the first place.
This is where the role of a fraud detection system comes into play.
Most digital payment processing platforms use:
- Rule-based checks – Setting up rules like transaction limits or blocking unusual locations
- Behavioural analysis – Looking for unlikely patterns that don’t match a user’s normal actions
- Risk scoring – Evaluation of each transaction is done before it is allowed to proceed
Through these systems, you can be careful of the red flags and block suspicious activities even before the transaction takes place.
Why Digital Payment Processing Platforms Matter for Businesses
Payment processing might happen in the background, but it has a direct impact on how businesses operate and grow. Be it customer experience or cash flow, handling of payments decides the fate of your operations.
A reliable payment processing platform impacts more than just transactions.
- Shapes the customer experience – Checkout processes are expected to be quick, trusted, yet flexible. If the payment processing system is smooth, then the chances of failed transactions and friction are reduced.
As the journey becomes comfortable, the user would want to come back again.
- Expanded sales and global reach – As the payment process gets easier, enabling mobile and international transactions also becomes convenient. This will help businesses reach a broader customer base. By offering multiple currencies, these platforms facilitate global expansions.
- Improved cash flow and operational efficiency – Online payments settle much faster than traditional methods like cheques. As the transaction takes only 1 to 3 business days to complete, the business’s cash flow is significantly improved.
Processing digital payments can be 57% less expensive on average than processing non-digital payments, where labour and other expenses are added on. This also gives businesses better visibility of their funds and provides them with more control over expenses
- Simplified record keeping – 16% of companies admit their vendor payments are consistently late due to manual approval lags. Payment processing systems simplify the tedious task of maintaining records. As everything is automated, manual work gets reduced, and so do the errors.
Final Thoughts
A tap, click, or card swipe sounds like simple actions, but they are actually carefully coordinated and include multiple systems, institutions and security layers that work together.
For businesses, understanding this flow is not just about payments. It is also about recognising the right framework which supports –
- Smoother customer experiences
- Stronger cash flow
- Better compliance
- Ability to scale without any operational issues
Businesses expand. Transactions increase. Payment system requirements increase.
When all this happens, a reliable digital payment processing platform becomes a business-critical foundation.
Platforms like Nook Pay operate further down the payment cycle. It helps businesses manage payouts, invoice validation, approvals, and settlements for vendors, affiliates, and partners.
As payment systems continue to grow, platforms don’t just process payments but also decide how money is distributed.
Help Centre
What is a digital payment processing platform, and how does it work?
A digital payment processing platform is the technology that securely authorises, verifies, clears, and settles electronic payments. It connects customers, businesses, banks, and networks to ensure money moves accurately from checkout to final settlement.
How does a digital payment processing platform ensure secure transactions?
Digital payment processing platforms use encryption, tokenisation, fraud detection systems, and PCI DSS compliance to protect sensitive payment data. These security layers help prevent unauthorised access while maintaining fast and reliable transaction processing.
What is the difference between payment authorisation, clearing, and settlement?
Authorisation checks if a payment is allowed, clearing confirms and records transaction details, and settlement is when funds are actually transferred. Each stage ensures accuracy, security, and agreement between all parties involved.
What types of businesses benefit most from digital payment processing platforms?
Digital payment processing platforms are ideal for online businesses, marketplaces, service providers, affiliate networks, and global vendors. Any organisation handling frequent, high-volume, or cross-border transactions benefits from automated processing, improved security, and streamlined payment operations.



